Pondering, Can a Battery Be Too Dead to Charge? Learn the surprising facts with our detailed exploration. Find out now!
Batteries are important in our daily lives. Have you ever tried to start your car in the morning only to find out that the battery is completely dead? You might think that all you need is a jump start or a charger, but what if your battery is too dead to charge?
Is it even possible? Can a Battery Be Too Dead to Charge? The answer is yes, it can be. But it’s not as simple as you might think. Different factors can affect how dead your battery is and whether it can be revived.
In this article, I will explain what causes a car battery to die, how to tell if it’s too dead to charge, and what you can do to prevent this from happening again. I know how frustrating dealing with a dead battery can be because I’ve been there myself. But don’t worry, I’ve got you covered. Read on to find out more.
Let’s talk shop!
| Issue | Investigation Steps | Possible Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Battery won’t start the car | – Check battery terminals for corrosion/loose connections – Use a multimeter to test. The voltage (should be 12.6V or higher when fully charged) – Check for signs of damage like bulging or leaks | – Clean terminals and tighten connections – Recharge battery using jumper cables or battery charger if voltage is low – Replace battery if severely damaged |
| Battery won’t hold a charge | – Use multimeter to test voltage after charging (should remain 12.6V or above) – Check for shorts like lights left on – Test each cell individually with a hydrometer | – Charge battery fully and allow to rest 24 hours – Address any electrical shorts/drains – Replace battery if it still won’t hold charge |
| Battery recharges but capacity seems reduced | – Note conditions like age of battery, extreme temps – Use carbon pile load tester to test capacity after full charge | – Charge and test capacity several times – Replace battery if capacity continues to drop |
| Battery is old or seems damaged | – Inspect battery case, terminals, and fluid for signs of damage – Note the battery’s age and conditions it’s been exposed to | – Try reconditioning old battery with slow charger – Replace battery if reconditioning doesn’t restore performance |
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Batteries can often be recharged, but certain factors determine success.
- A battery’s type and drainage severity impact its ability to recharge.
- Understanding battery behavior helps determine if a dead battery is recoverable.
Can a Battery Be Too Dead to Charge – Understanding Battery Charge
A battery’s charge and discharge cycle significantly affects its lifespan. When a battery loses charge and falls below a certain voltage, it can be challenging to recharge it. The battery may receive some charge, but its overall capacity, its ability to hold that charge, will be impaired.
Even if the battery is completely dead, it can often still be recharged. But this may take a lot of effort and time. Even after reconditioning, the battery’s power may only recover up to 70%.
But why does this happen? Let’s explain.
Sulfation is a common cause of battery failure that occurs when the battery is not fully charged, causing sulfuric acid crystals to form on the battery plates. This can reduce the battery’s ability to hold a charge and ultimately lead to its failure.
To make your batteries last longer and work better, avoid letting them get too low and keep them fully charged. You can do this by keeping an eye on the battery’s charge level and recharging it before it gets too low.
This prevents sulfation and other types of damage to the battery and makes sure that it functions well for a long time.
Determining Battery ‘Death’
When we talk about a battery being “dead,” we usually mean it no longer has enough power to start a vehicle. But can a battery truly reach a point where it’s impossible to charge again? Well, yes, it can.
Let’s dive into the factors that determine a battery’s “death.”
Here are some telltale signs:
- The vehicle won’t start, or the engine cranks weakly.
- Lights and other electrical accessories don’t work.
- The battery case is bloated, swollen, or looks damaged.
- A multimeter shows a voltage level significantly below the standard amount.
Did you know that batteries can also die due to age, improper use, or extreme temperatures?
If you find your battery is within the “dead zone,” a jump start might be able to bring it back to life. It’s worth a try, right?
If it still doesn’t work after that or can’t hold a charge, you may need to replace it entirely.
The Science Behind Dead Batteries
But you might have noticed that none of that answers the question of what causes a dead battery.
Let’s look at the process in more detail.
Lead-acid batteries operate based on a series of chemical reactions. Here’s the lowdown:
- Discharging: When the battery is in use (i.e., discharging), the lead (Pb) in the negative plate reacts with the sulfuric acid (H2SO4) in the electrolyte to form lead sulfate (PbSO4) and hydrogen ions (H+). The hydrogen ions then react with the lead dioxide (PbO2) in the positive plate to form water (H2O) and lead sulfate (PbSO4).
- Recharging: During recharging, the lead sulfate (PbSO4) on both plates is converted back into lead (Pb) on the negative plate and lead dioxide (PbO2) on the positive plate. The sulfuric acid (H2SO4) in the electrolyte is also replenished.
But over time, several things might cause a lead-acid battery to become “dead” or unable to hold a charge:
- Sulfation: If a lead-acid battery is left discharged for an extended period, lead sulfate crystals can form on the plates and harden, reducing the battery’s capacity.
- Electrical shorting: The positive and negative electrodes (plates) must not touch each other. If they do, they immediately short out, and the cell dies.
- Active material shedding: In flooded lead-acid batteries, the active paste applied to the plates gradually falls off as part of the physical wear and tear when chemical reactions take place.
- Temperature Extremes: Lead-acid batteries are designed to work in a fairly large range of temperatures, but performance suffers in both cold and hot environments.
It’s also worth noting that sometimes a battery might appear dead due to other issues, such as problems with the alternator in a car, rather than the battery itself. Always ensure to check the actual condition of the battery before assuming it’s dead.
How to Tell if Your Battery Is Dead
Let’s go through some steps we can take to get a good idea if your car battery is dead:
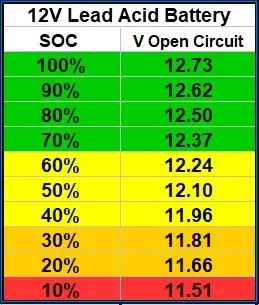
- Use a Multimeter: A multimeter is a device that can measure electrical voltage, current, and resistance. To test a car battery with a multimeter:
- Set the multimeter to measure DC voltage and set the dial to 20, allowing you to measure between 0-20 volts accurately.
- Connect the red probe to the positive terminal and the black probe to the negative terminal.
- A good, healthy car battery should have no fewer than 12.6 volts. If the battery goes down to 12.2V, it’s actually only 50% charged, and below 12V, it’s classed as discharged.
- Check for Signs of a Dead Battery: Some signs of a dead or dying battery include difficulty starting your car, dim headlights, battery light on your dashboard, and a battery that’s old, leaking, corroded, or swollen.
- Inspect the Battery Case: Check for any deformities such as cracks in the casing, any bulging of the cells, and if there is a leak of fluid.
- Test for Dead Cells: If you have access to the battery’s individual cells, you can use a hydrometer-style battery tester that measures the specific gravity of the battery acid. This can tell you whether any cells are ‘dead’ or not.
Remember, always follow safety guidelines when handling car batteries. If you’re unsure, it’s best to seek help from a professional.
Common Causes of Battery Death
Car batteries have a limited lifespan and can die for various reasons. It can be frustrating to deal with a dead battery, especially when you need your car the most.
Let’s discuss some of the most common causes of battery death.
Loose or corroded connections
Loose or corroded connections can cause a battery to fail. When the terminals are not connected correctly, the flow of electricity is affected. This can cause the battery to lose its charge. To prolong the life of your car battery, ensure the battery connections are clean and tight.
Persistent Electrical Drains
Another common reason for a dead battery is persistent electrical drains. Sometimes, the electronics in your car can use power even when the car is off. This can happen with the security system or if there are broken lights. This can lead to a dead battery over time.
Extreme Temperatures
Extreme weather conditions can also affect the battery’s life. Hot or cold temperatures can cause your battery to work harder and lead to a shorter lifespan. Batteries can die faster in cold weather as the chemical reactions can slow down.
Your Driving Habits
Driving habits can also have an impact on the life of your car battery. Frequently starting and stopping your car can cause your battery to drain faster. Using power windows, air conditioning, and the radio in your car drains the battery.
Your vehicle needs to recoup the charge lost by standing idle and starting your car. If you only drive to the shops and while using all of your appliances, it can struggle to do this. Every now and again, open it up on the highway or interstate and give it a proper boost.
Alternator Issues
Lastly, an alternator that’s not charging the battery properly can cause it to die. A faulty alternator, loose cables, or a problem with the voltage regulator can all add to this issue. If your alternator is not working right, you should have a professional check and fix it.
Age
Finally, no battery can hold back the sands of time or last forever. After around 4-5 years, most lead acid batteries are done.
Procedures to Recharge a Dead Battery
But how can we recharge our dead batteries? Glad you asked!
Here’s how to do it.
Using another vehicle
First, make sure to park another working car nearby. Turn off both cars and open their hoods.
Next, connect the red clamp of the jump starter to the positive terminal on your dead battery. Do the same with the black clamp on the negative terminal. Then, repeat the process for the battery in the other car.
Now, start the donor vehicle and let it idle for a few minutes. This allows the dead battery to gain some charge. After that, try starting your car. If it starts, let it run for a while to recharge the battery. You may need further help or a new battery if it doesn’t start.
Using a Portable Jump Starter
A portable jump starter can be a lifesaver if another vehicle isn’t available. Connect the red clamp to the positive terminal and the black clamp to the negative terminal of your dead battery.
Power on the jump starter and wait for a few minutes. Then, try to start your car.
If successful, let the engine run to recharge the battery. Remember to follow the manufacturer’s instructions when using a portable jump starter to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Using a Battery Charger
Another way to recharge a dead battery is by using a battery charger. First, make sure your car is turned off. First, attach the red clamp of the charger to the positive battery terminal. Then, connect the black clamp to the negative terminal. Give the clamps a little wiggle to ensure they have a good connection.
After that, plug in the charger and set it to the correct voltage and amperage for your battery. If unsure, check your car’s manual for the correct settings. Let the battery charge for a few hours or overnight, depending on its condition. During this time, keep an eye on the battery’s temperature, ensuring it doesn’t get too hot.
Once the battery reaches a voltage of 11.5V or higher, it’s ready to be reconnected to your car and tested. After recharging, a dead battery may only regain about 70% of its original power. So, consider replacing the battery if it struggles to hold a charge.
Safety Precautions While Charging
I want to discuss the safety precautions we should take while charging a dead battery. A battery may not be chargeable if it’s too dead or damaged from discharging. But in cases where the battery can still be charged, safety comes first.
First, use the correct charger for the specific battery type. Mixing different brands of rechargeable batteries in a charger might be dangerous.
The main dangers are hydrogen gas and sulfuric acid formation in the liquid. To prevent a fire or explosion, don’t charge batteries near flames or ignition sources. Hydrogen gas is flammable. I advise that you charge your vehicle outside or in a well-ventilated area to avoid the build-up of these gasses.
Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for battery charging. To charge the battery safely, check it, disconnect the charger when it’s full, and always check for damage before and after charging.
Before You Go…
Now you know why some batteries can’t be charged and what affects their ability to recharge. But how do you know whether your battery is in that situation? How do you test your battery to determine its charge and health? The answer is simple: you use some tools and techniques that I will teach you in my next article: “How to Test a Car Battery”.
I will show you how to measure the voltage, current, and specific gravity of your battery cells. You can use a multimeter, load tester, or battery hydrometer. These readings will tell you what state your battery is in.
They will also help you identify any problems with your battery, such as a bad cell, a short circuit, or a sulfation. Don’t let your battery surprise you, and read this article to learn how to test it easily and accurately.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here’s the FAQs
Can a battery be so dead it won’t hold a charge?
Yes, a battery can be so dead that it won’t hold a charge. This happens when the battery discharges too much, causing internal damage. The deeper the discharge, the more difficult it becomes to restore the battery’s life.
How to revive a car battery that won’t charge?
To revive a car battery that won’t charge, try jump-starting it. Connect jumper cables to a working battery and the dead battery. Start the vehicle with a working battery, allowing it to run for a few minutes. This may help recharge the dead battery. Check your vehicle’s manual for specific instructions.
How to bring a dead lead-acid battery back to life?
To restore a dead lead-acid battery, try these steps:
- Clean the terminals with a wire brush to remove corrosion.
- Fill the battery cells with distilled water.
- Connect a battery charger and charge the battery slowly for 24 hours.
- Disconnect the charger and let the battery rest for another 24 hours.
- Test the battery voltage to see if it holds a charge.
Remember, success isn’t guaranteed, and results may vary.
Will a car battery recharge if you let it sit?
A car battery won’t automatically recharge if you let it sit. Instead, it will slowly discharge over time. To recharge a car battery, you can connect it to a charger. Alternatively, you can jump-start the vehicle and let the alternator charge it. Do not leave a dead battery unattended for long, as it may cause permanent damage.
Can a battery be too old to charge?
Yes, a battery can be too old to charge. As batteries get old, they can have problems like sulfation and internal corrosion. These problems make it harder for the batteries to stay charged. If a battery is old or damaged, it might not recharge anymore. In this case, it’s best to replace it.
Related Articles
- What Causes A Dead Cell In Car Batteries? 3 Proven Reasons Revealed!
- What is More Important: Volts or Amps for Charging? Don’t Let Slow Charging Hold You Back
- The common causes of battery failure – 5 Surprising Reasons Revealed
- What Happens to the Battery If You Don’t Drive Your Car for 3 Months: Complete Guide


